Rogue ONTs
A rogue ONT refers to an unauthorized or unapproved Optical Network Terminal connected to a passive optical network (PON) without the knowledge or permission of the service provider. It can occur due to unauthorized connections, fraudulent activity, or misconfiguration. Rogue ONTs pose risks such as network security vulnerabilities, degraded service quality, service abuse, and network instability. Service providers employ measures such as monitoring the network, authentication, and authorization processes, and remedial actions to address rogue ONTs.
How to Detect Rogue ONTs
To detect rogue ONTs, the ability to decode upstream messages is needed, which is why the MTTplus-420 is recommended. However, the detection of rogue ONTs also depends on the capabilities of the equipment used. The FX120, for example, lacks upstream decoding capabilities required for rogue ONT detection. Despite that, the FX120 can still report rogue activity if the OLT has rogue detection capabilities and sends specific commands to shut down the ONT.
When testing for rogue ONTs, the FX120 should be placed after the last splitter and right before the ONT to capture downstream information. The OLT will send messages to request ONTs to shut down if they are transmitting outside their timeslot. The FX120 analyzes PLOAM messages, such as disable_SN or emergency_stop, sent from the OLT to the ONT to detect rogue activity. Upon multiple tests that were conducted to determine the time required for proper rogue detection, it was found that the unregistration and disabling of ONTs were instant, yet it could take up to 15 mins to reenable all except the rogue ONT.
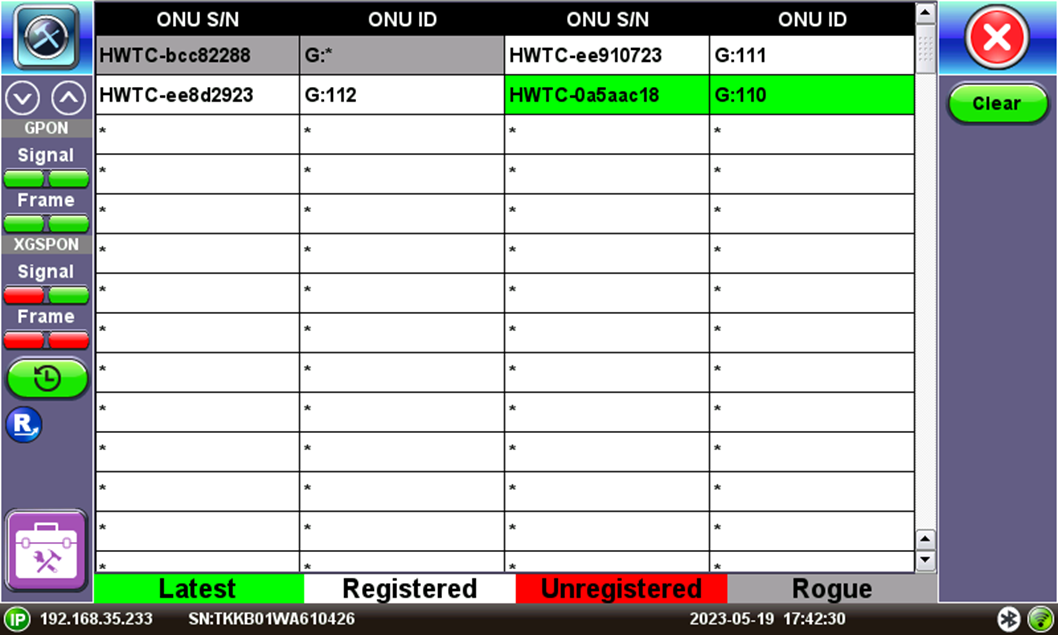
Rogue ONT Detection