Service Level OAM: 8021ag/Y.731G/8113.1 Setup
Under the Service Level OAM tab, the user has the option of starting the 802.1ag, Y.1731, or G.8113.1 test.
-
Fill out the given parameters.
MD Name, MA Name, VLAN, and MD Level input values must match for both connected OAM devices in order for the test to work. The Destination MEPID and Local MEP ID must also be inverted for the tests to work.
-
Tap the box next to 802.1ag, Y.1731, or G.8113.1 to start the selected test. The transmission of OAM PDUs become active as soon as the checkmark is added to the test.
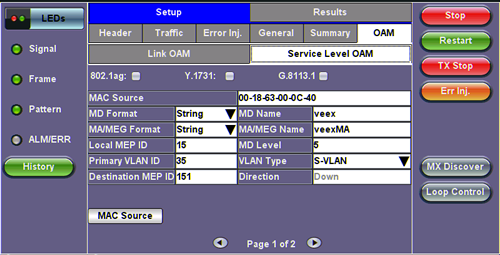
OAM - Service Level OAM (Page 1)
Service Level OAM Configuration Parameters
-
MAC Source: Enter the source address of the test set or tap the MAC Source button to assign a default MAC address.
-
MD Format: Configure the format of the Maintenance Domain Name:
-
None: No Maintenance Domain name
-
MAC+2octet: User configurable MAC address + 2 octets
-
String: User configurable ASCII character string
-
-
MD Name: Name of the Maintenance Domain (only for 802.1ag)
-
MA/MEG Format: Configure the format of the Maintenance Association name:
-
VID: User configurable ASCII character string
-
String: User configurable ASCII character string
-
2 octet: 2 octet integer
-
ICC-Based: User configurable ITU-T Y.1731 ITU Carrier Code (ICC) based
-
-
MA/MEG Name: Enter the name of the 802.1ag MA or Y.1731 MG
-
Local MEP ID: Local end point identifier along the path (1 to 8191)
-
MD Level: Maintenance domain level (0 to 7)
-
MEP ID: End point identifier (1 to 8191)
-
Primary VLAN ID: VLAN ID associated with the MA or MEG
-
VLAN Type: C-VLAN, S-VLAN, or None
-
Destination MEP ID: MEP ID of the MEP end point
-
Direction
-
Up: Inward facing MEP used for MA/MEG with a wider reach (i.e., end-to-end, beyond a single link)
-
Down: Outward facing MEP used for MA/MEG spanning a single link
-
|
|
Differences between 802.1ag, Y.1731, and G.8113.1 Selecting 802.1ag enables Continuity Check Messages (CCM), Loopback Message (LBM) and Link Trace Message (LTM). ITU-T Y.1731 provides all of the 802.1ag functionality with additional performance monitoring capabilities including Frame Loss (LM), and Delay (DM). ITU-T G.8113.1 provides further monitoring of MPLS-TP traffic. |
IEEE 802.1ag Definitions
-
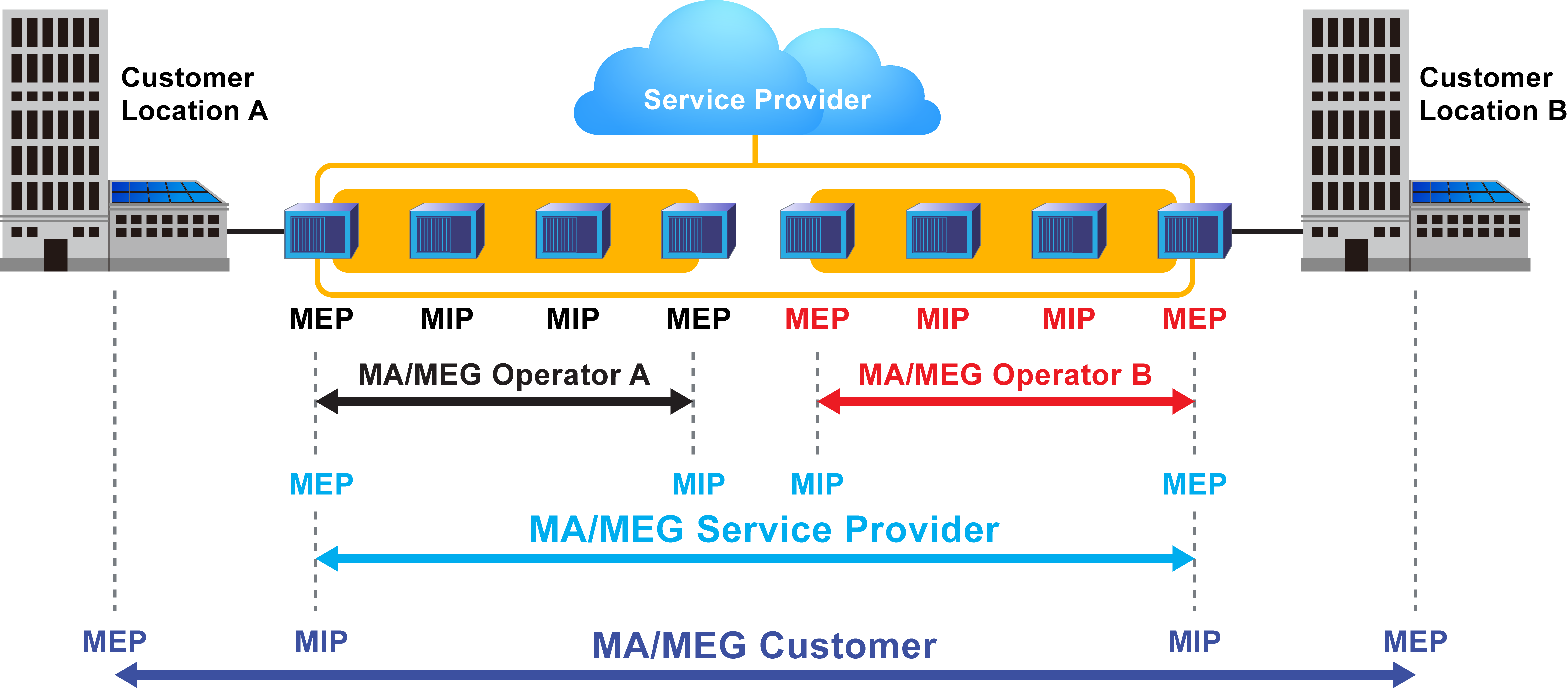
Maintenance Domain (MD) : Management space on a network that is owned and operated by a single network provider. There is a maintenance level (from 0 to 7) to define the hierarchical relationship between domains. Maintenance domains can be nested but never intersect. MD is defined by Operational or Contractual Boundaries (e.g., Customer/Service Provider/Operator).
-
Maintenance Association (MA): Association of Maintenance. Elements that comprise the Maintenance domain.
-
Maintenance Elements can either be MEPs (End points) or MIPs (Intermediate Points)
-
MEPs are at the edge of the network. They can generate and respond to OAM messages. A point-to-point EVC has only 2 MEPs, a multi-point EVC has multiple MEPs.
-
MIPs are located between the MEPs and can be used to isolate network problems. MIPs cannot generate OAM messages but can respond.
-
-
Maintenance Level: Identifies the network hierarchy. Higher Level = Largest network. Level information present in all OAM PDU frames.
-
Level 0,1,2 = Operator domain
-
Level 3,4 = Service Provider domain
-
Level 5,6,7 = Customer domain
-
Some terms differ between IEEE 802.1ag and ITU Y.1731 protocols.The chart below describes the differences.
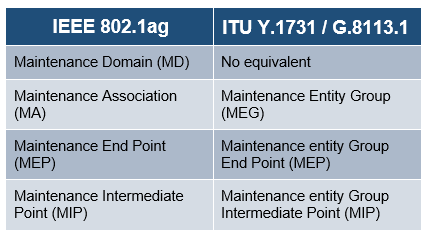
Definition Equivalencies
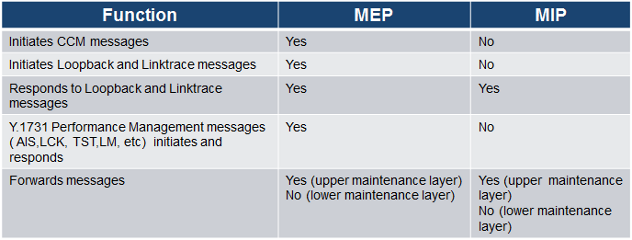
Maintenance Point Roles