Accessing Jitter and Wander
Go to OTN/SDH/SONET Testing from the Test Mode Selection, then select the following:
-
For PDH or DS3/1 signals: Home (Main Menu) > PDH or DS3/1 Tools > (DS1/3) Jitter & Wander
-
For SONET or SDH signals: Home (Main Menu) > SONET/SDH Tools > More > Jitter & Wander
Jitter & Wander displays the Jitter Measurements showing measurements and analysis of jitter in received signal.
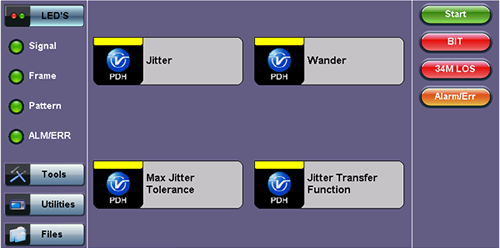
Jitter and Wander (PDH E3 Menu)
Jitter and Wander are usually described as the phase noise in digital signals. This is a natural occurrence in telecommunication networks.
Excessive jitter can lead to transmission errors and deterioration in network quality. ITU defines jitter as follows: "The short-term variations of the significant instances of a digital signal from their ideal positions in time (where short-term implies these variations are of frequency greater than or equal to 10 Hz)." The long-term variation (less than 10 Hz) of a digital signal is called wander.
In simple terms, jitter is an unwanted phase modulation of the digital signal that may cause errors or bit slips in a digital circuit and deteriorate the performance of a transmission network.
In lower-rate digital systems, systematic jitter is dominant. In higher-rate systems, random jitter may become more important. Test environment parameters that affect jitter performance are test sequences, bit rate, pulse shape, cable characteristics, temperature, cross-talk, and noise.